From the excellent documentary film, "I Am Not Your Negro."
Happy Juneteenth everybody!
Commentary and analysis on American politics, culture, and national identity, U.S. foreign policy and international relations, and the state of education - from a neoconservative perspective! - Keeping an eye on the communist-left so you don't have to!
At Amazon, Ilisa Barbash, Molly Rogers, and Deborah Willis, eds., To Make Their Own Way in the World: The Enduring Legacy of the Zealy Daguerreotypes.
Following-up, "Harvard University Pledges $100 Million to Redress Past Ties to Slavery (VIDEO)."
At the New York Times, "The First Photos of Enslaved People Raise Many Questions About the Ethics of Viewing."
This is Renty below, in a very famous photograph you may have seen before.
From the article:
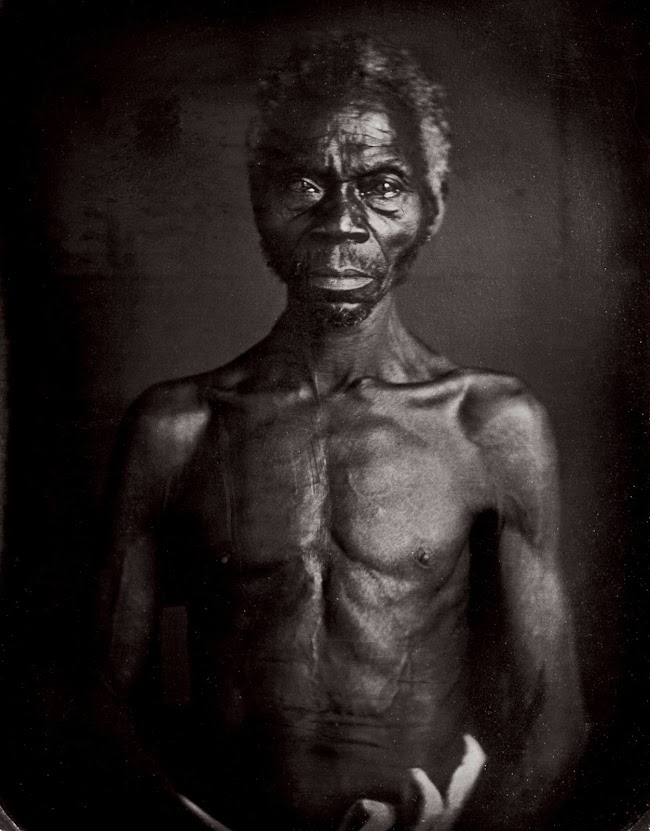
For a century, they languished in a museum attic. Fifteen wooden cases, palm-size and lined with velvet. Cocooned within are some of history’s cruelest, most contentious images — the first photographs, it is believed, of enslaved human beings. Alfred, Fassena and Jem. Renty and his daughter Delia. Jack and his daughter Drana. They face us directly in one image and stand in profile in the next, bodies held fixed by an iron brace. The Zealy daguerreotypes, as the pictures are known, were taken in 1850 at the behest of the Harvard zoologist Louis Agassiz. A proponent of polygenesis — the idea that the races descended from different origins, a notion challenged in its own time and refuted by Darwin — he had the pictures taken to furnish proof of this theory. Agassiz wanted images of barbarity, and he got them — implicating only himself. He had hand-selected his subjects in South Carolina, seeking types — “specimens,” as he put it — but each daguerreotype reveals an individual, deeply dignified and expressive. Their hurt, contempt, fatigue, utter refusal are unequivocal. The photographer, Joseph T. Zealy, who specialized in society portraits, did not alter his method for the shoot; he carried on as usual, using the same light, the same angles, giving the images their unsettling, formal perfection. Agassiz showed the pictures only once. They were then tucked away at Harvard’s Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology. Rediscovered in 1976, they have been at the center of urgent debates about photography ever since...
Ooo!
Well one would think. They're sitting on a $53.2 billion endowment. I'm sure they can afford a chintzy $100 million to throw a sop for reparations. *Eye Roll.*
At the New York Times, "Harvard Details Its Entanglements With Slavery and Its Plans for Redress."
Plus, "The Major Findings of Harvard’s Report on Its Ties to Slavery":Harvard University issued a 134-page report investigating its ties to slavery, and its legacy. Here are the key findings. In 2019, Harvard’s president, Lawrence S. Bacow, appointed a committee of faculty members to investigate the university’s ties to slavery, as well as its legacy. Discussions about race were intensifying across the country. Students were demanding that the names of people involved in the slave trade be removed from buildings. Other universities, notably Brown, had already conducted similar excavations of their past. The resulting 134-page report plus two appendices was released Tuesday, along with a promise of $100 million, to create an endowed fund to “redress” past wrongs, one of the biggest funds of its kind. Here are some of its key findings and excerpts. Slavery Was Part of Daily Life at the University The report found that enslaved people lived on the Cambridge, Mass., campus, in the president’s residence, and were part of the fabric, albeit almost invisible, of daily life. “Over nearly 150 years, from the university’s founding in 1636 until the Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court found slavery unlawful in 1783, Harvard presidents and other leaders, as well as its faculty and staff, enslaved more than 70 individuals, some of whom labored on campus,” the report said. “Enslaved men and women served Harvard presidents and professors and fed and cared for Harvard students.” Four Harvard Presidents Enslaved People The committee found at least 41 prominent people associated with Harvard who enslaved people. They included four Harvard presidents, such as Increase Mather, president of the university from 1692 to 1701, and Benjamin Wadsworth, president from 1725 to 1737; three governors, John Winthrop, Joseph Dudley and John Leverett; William Brattle, minister of First Church, Cambridge; Edward Wigglesworth, professor of divinity; John Winthrop, professor of mathematics and natural philosophy; Edward Hopkins, founder of the Hopkins Foundation; and Isaac Royall Jr., who funded the first professorship of law at Harvard. The University Benefited From Plantation Owners While New England’s image has been linked in popular culture to abolitionism, the report said, wealthy plantation owners and Harvard were mutually dependent for their wealth. “Throughout this period and well into the 19th century, the university and its donors benefited from extensive financial ties to slavery,” the report said. “These profitable financial relationships included, most notably, the beneficence of donors who accumulated their wealth through slave trading; from the labor of enslaved people on plantations in the Caribbean islands and in the American South; and from the Northern textile manufacturing industry, supplied with cotton grown by enslaved people held in bondage. The university also profited from its own financial investments, which included loans to Caribbean sugar planters, rum distillers, and plantation suppliers along with investments in cotton manufacturing.” Integration Was Accepted Slowly Early attempts at integration met with stiff resistance from Harvard leaders who prized being a school for a white upper crust, including wealthy white sons of the South. “In the years before the Civil War, the color line held at Harvard despite a false start toward Black access,” the report said. “In 1850, Harvard’s medical school admitted three Black students but, after a group of white students and alumni objected, the school’s dean, Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr., expelled them.” Faculty Members Spread Bogus Science Harvard faculty members played a role in disseminating bogus theories of racial differences that were used to justify racial segregation and to underpin Nazi Germany’s extermination of “undesirable” populations. “In the 19th century, Harvard had begun to amass human anatomical specimens, including the bodies of enslaved people, that would, in the hands of the university’s prominent scientific authorities, become central to the promotion of so-called race science at Harvard and other American institutions,” the report said. The bitter fruit of those race scientists remains part of Harvard’s living legacy today... The Legacy of Slavery Lived On Until as recently as the 1960s, the legacy of slavery lived on in the paucity of Black students admitted to Harvard...
At Amazon, Douglas Blackmon, Slavery by Another Name: The Re-Enslavement of Black Americans from the Civil War to World War II.
Actually it's Ibram Henry Rogers, so I guess that's more authentic, considering his shtick.
Shoot, I'm surprised he doesn't wear a dashiki. *Shrug.*
At New York magazine, "How Anti-Racist Is Anti-Racism?":
Ibram X. Kendi’s work takes dead aim at those convenient fictions [of the mainstream interpretations of U.S. history]. The historian and pop-theoretician of “antiracism” seeks to disrupt white America’s complacency about racial progress by spotlighting Black-white disparities in incarceration, wealth, and other social ills. And he seeks to stigmatize victim-blaming accounts of Black social disadvantage by insisting that all racial disparities derive from a history of white supremacy (not a “culture of poverty”). Kendi is especially concerned with the way superficially non-racist ideas and policies can serve the function of fortifying racial hierarchy. His solution is to adopt a consequentialist definition of racism: A policy or idea is racist to the extent that it “produces or sustains racial inequity,” and antiracist to the extent that it reduces the same. Kendi’s ideas have both influenced and internalized broader intellectual currents on the social-justice left. And, collectively, antiracist thinkers and activists have had great success in reshaping mainstream discourse. Today, statistical testaments to racial inequity are a staple of Democratic oratory, while pathologizing calls for Black men to “pull up their pants” and raise their children are largely absent. Mainstream news outlets, meanwhile, rarely report on social problems without conveying pertinent racial disparities. And much of corporate America has invested resources into monitoring and mitigating racial gaps in pay, hiring, and promotions. All of which is to the good. Today’s discourse about race is surely more conducive to egalitarian reform than yesterday’s (better for the liberal media to fixate on racial disparities than “welfare queens”). Given that anti-Black discrimination in hiring remains prevalent in the U.S., corporations that feel compelled to diversify their workforces for brand reputation’s sake are preferable to ones that don’t. Further, one could reasonably argue that Kendi-esque antiracist advocacy has already facilitated meliorative changes in public policy. Had such advocates not heightened the salience of racial inequity among white liberals, debt relief for disadvantaged Black farmers might not have made it into The American Recovery Act. And it’s also plausible that antiracists’ stigmatization of “welfare queen” narratives enabled the Democratic Party’s recent embrace of unconditional cash assistance to low-income families; until this year’s CTC expansion, Democrats had designed their anti-poverty programs to leave out America’s poorest children so as to punish their parents for being unemployed, a convention that disproportionately harmed Black families. This said, the scale of reform necessary for eradicating Black disadvantage remains far beyond the bounds of political possibility. Enact Joe Biden’s entire agenda, and millions of African Americans will still lack affordable housing, remunerative employment, and health insurance. Meanwhile, an increasingly authoritarian far-right party controls a majority of U.S. states, and is well-positioned to retake Congress, if not full control of the federal government, within the next four years. Building the America that the Civil Rights Movement demanded — one that would guarantee economic security to all of its citizens — will require transforming our nation’s politics. Within blue America, there is much debate about whether the discourse of antiracism is conducive to such a transformation...
At Amazon, Fergus Bordewich, Bound for Canaan: The Epic Story of the Underground Railroad, America's First Civil Rights Movement.
At Amazon, Robert Woodson, Ed., Red, White, and Black: Rescuing American History from Revisionists and Race Hustlers.
"Walkin' On The Sun"
John Sexton, at Hot Air, "University of Chicago postpones course on the problem of whiteness..."
Mary Chastain, at Legal Insurrection, "‘Deplatforming Works’: Ocasio-Cortez Celebrates Fox News and Tucker Carlson Parting Ways..."The Other McCain, "How to Translate Bidenese..."